The IF function is one of the most commonly used functions in Excel. It allows you to make logical comparisons between a value and what you expect. An IF statement can have two results: the first result is if your comparison is True, and the second result is if your comparison is False.
Syntax
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| =IF(logical_test, value_if_true, value_if_false) | Checks, whether a condition is met, returns one value if true and another value if false. |
Arguments:
- logical_test: The condition you want to test.
- value_if_true: The value to return if the condition is true.
- value_if_false: The value to return if the condition is false.
Example
Here is a more complex example of the IF function in action. Imagine you have a table of students' scores, and you want to assign grades based on their scores:
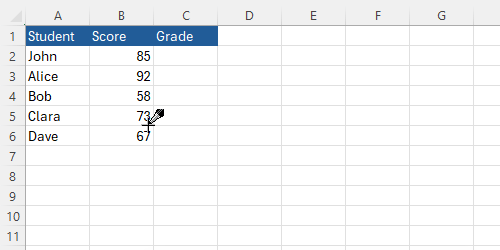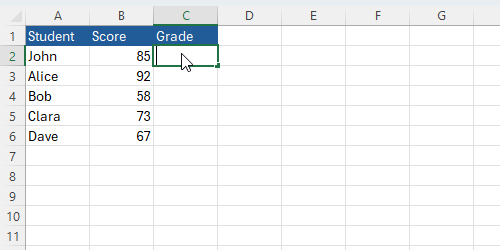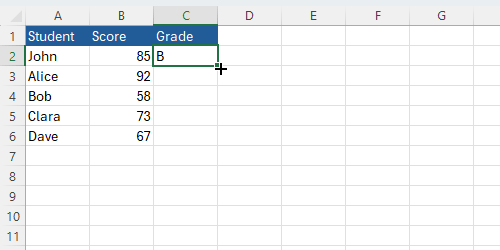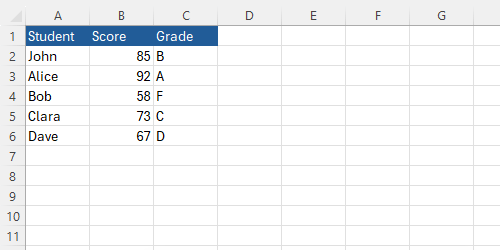
You can use the following formula to assign grades:
=IF(B2>=90, "A", IF(B2>=80, "B", IF(B2>=70, "C", IF(B2>=60, "D", "F"))))Below is an animated GIF showing how to apply this formula:
Exercises
Exercise 1
Task: Create a table of employees with their hours worked and determine if they have worked overtime. An employee works overtime if they work more than 40 hours in a week.
Exercise 2
Task: Create a table for a small business's monthly sales and determine if each month meets the sales target. The sales target is $10,000.
Solutions
The Solution to Exercise 1
Determine if the employees have worked overtime (40 hours):
=IF(B2>40, "Yes", "No")
=IF(C2>40, "Yes", "No")
=IF(D2>40, "Yes", "No")
=IF(E2>40, "Yes", "No")
=IF(F2>40, "Yes", "No")The Solution to Exercise 2
To check if each month meets the sales target:
=IF(B2>=10000, "Yes", "No")
=IF(C2>=10000, "Yes", "No")
=IF(D2>=10000, "Yes", "No")
=IF(E2>=10000, "Yes", "No")
=IF(F2>=10000, "Yes", "No")